|
⇤ ← Revision 1 as of 2010-01-06 21:37:13
Size: 709
Comment:
|
Size: 734
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 2: | Line 2: |
| Various algorithms in EMAN2 will depend non-linearly on the box size of the particle. Sometimes (such as the case with FFTs), this behavior will appear bizzare. For example refinements with a box size of 45 pixels will run roughly twice as fast as those with a box size of 47, and 44 is about 20% faster than 45. | |
| Line 3: | Line 4: |
| Various algorithms in EMAN2 will depend non-linearly on the box size of the particle. Sometimes (such as the case with FFTs), this behavior will appear bizzare. For example refinements with a box size of 45 pixels will run roughly twice as fast as those with a box size of 47, and 44 is about 20% faster than 45. |
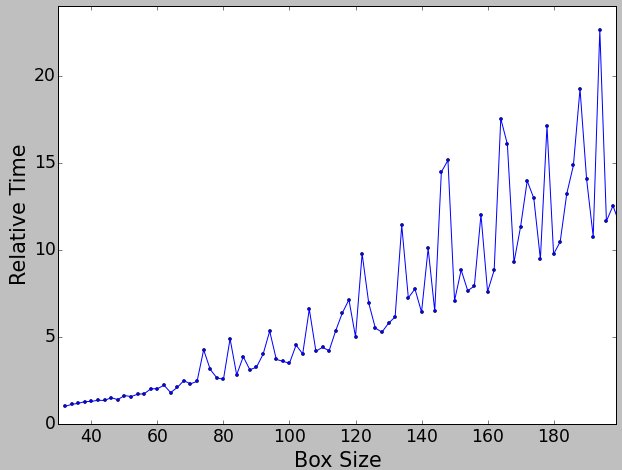
The following plot shows how long it takes to compute one similarity matrix element for a noisy particle aligned to a noise-free reference with the rotate-translate-flip aligner, refine alignment enabled with the dot comparator, and a phase residual for a similarity metric. ie - typical options for a real refinement: |
| Line 7: | Line 6: |
| The following plot shows how long it takes to compute one similarity matrix element for a noisy particle aligned to a noise-free reference with the rotate-translate-flip aligner, refine alignment enabled with the dot comparator, and a phase residual for a similarity metric. ie - typical options for a real refinement: |
{{attachment:rel_time.jpg}} |
| Line 11: | Line 8: |
| [[attachment:rel_time.jpg]] | [[attachment:rel_time.jpg|]] |
Particle Box Size and Speed
Various algorithms in EMAN2 will depend non-linearly on the box size of the particle. Sometimes (such as the case with FFTs), this behavior will appear bizzare. For example refinements with a box size of 45 pixels will run roughly twice as fast as those with a box size of 47, and 44 is about 20% faster than 45.
The following plot shows how long it takes to compute one similarity matrix element for a noisy particle aligned to a noise-free reference with the rotate-translate-flip aligner, refine alignment enabled with the dot comparator, and a phase residual for a similarity metric. ie - typical options for a real refinement: