|
Size: 4167
Comment:
|
Size: 5762
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 34: | Line 34: |
| The program will start from the initial orientation assignment and run five iterations of refinement using GMMs as references. After the refinement, the resolution should reach ~3.4Å | The program will start from the initial orientation assignment and run five iterations of refinement using GMMs as references. It should create a folder called '''gmm_00''', and you can find all files related to the refinement inside. '''threed_xx.hdf''' are the reconstructed density maps, '''fsc_masked_xx.txt''' are the FSC curves, and '''model_xx_even/odd.txt''' are the GMM parameters after each iteration. After the refinement, the resolution should reach ~3.4Å. |
| Line 36: | Line 36: |
| {{attachment: global_refinement.png}} | {{attachment:global_refinement.png | structure after global refinement |width=600}} |
| Line 41: | Line 41: |
| Starting from a finished global refinement, run | Here we target the RBD using focused refinement. First, we need to make a mask for the target region using '''Filtertool'''. In the e2display browser, select '''gmm_00/threed_05.hdf''' and click '''Filtertool''' to start the program. Hold Shift while clicking the button will enter a "safe mode" of Filtertool, which might be useful if the program crashes often. To craft a mask for the RBD, we use three processors: |
| Line 43: | Line 43: |
| e2gmm_refine_new.py gmm_XX/threed_XX.hdf --startres X --npt N --mask mask.hdf --masksigma | mask.soft:dx=10.0:dy=15.0:dz=70.0:outer_radius=20.0:width=30.0 filter.lowpass.gauss:cutoff_abs=0.1 mask.auto3d.thresh:nshells=4:nshellsgauss=4:return_mask=True:threshold1=5.5:threshold2=3.0 |
| Line 46: | Line 48: |
| Here `mask.hdf` is a mask focusing on the target region. It is recommended to create this using Filtertool. | `mask.soft` locates the rough location of one of the RBD, and `filter.lowpass.gauss` lowpass filters the density map. `mask.auto3d.thresh` creates the final mask based on the filtered density. Basically, it starts from a high threshold indicated by `threshold1`, at which only the density of the target domain is visible, and get down to a lower `threshold2`, where the density in the target domain is connected, but the density outside is not. The processor will then include all densities at `threshold2` that are connected to the visible voxels at `threshold1`, pad a few layer and add a soft Gaussian falloff as indicated by `nshells` and `nshellsgauss`, then return the mask. {{attachment:craft_mask.png | craft mask using filtertool |width=500}} Clicking '''File -> Save''' will save the results to '''processed_map.hdf''', and we rename it to '''mask_rbd.hdf''' for better bookkeeping. |
Particle orientation refinement using GMM representation
- Most programs are available in EMAN2 builds after 2023-03, but some are still under continuous development. Newer versions are typically better.
- It is recommended to add the "examples/" folder in EMAN2 binary to $PATH, as some new programs have not been moved to "bin/" yet.
- The tutorial is only tested on Linux with Nvidia GPU and CUDA.
Here we use particles of SARS-COV-2 from EMPIAR-10492 as an example. Starting from particles with assigned orientation, i.e. the Polished folder (13.5GB) from EMPIAR, as well as job096_run_data.star.
Import existing refinement
Here we will need a .lst file with the location of all particles and their initial orientation assignment. Since here we start from a Relion star file, run
e2convertrelion.py job096_run_data.star --voltage 300 --cs 2.7 --apix 1.098 --amp 10 --skipheader 26 --onestack particles/particles_all.hdf --make3d --sym c3
Note that we need to phase flip the particles before the refinement, so this may take a while. Also make sure to provide the correct CTF related information to the program, including voltage, cs, amp, apix, since the program does not read those from the star file automatically. Check --help for more details. After importing the particles, with the --make3d option, the program will create a r3d_00 folder and reconstruct the 3D maps. You should see the structure of Covid spike with FSC at ~3.9Å at this point. Note the resolution number here is different from the one reported, because the pixel size used for processing is 1.098, which is then calibrated to 1.061. We still use the pixel size of 1.098 here, since otherwise the CTF information from the star file would be incorrect.
To start from other formats:
From classical EMAN2 refinement (e2refine_easy), run e2evalrefine.py refine_XX --extractorientptcl particles.lst
From the new EMAN2 refinement (e2spa_refine), simply use the ptcls_XX.lst file from the last iteration.
From CryoSPARC or others, convert it to a relion star file using pyem, then follow the relion conversion.
Global orientation refinement
We first need to determine the number of Gaussian to represent the volume. Often it is convenient to just use the number of non-H atoms in the molecule. Alternatively, we can guess the number given an existing map, isosurface threshold, and target resolution.
e2gmm_guess_n.py r3d_00/threed_00.hdf --thr 4 --maxres 3.5 --startn 10000
Here the number we get is 18000, and the program should also generate a file called threed_seg.pdb which can be used to visualize the coordinates of the Gaussian in the density map, and also used to initialize the GMM for refinement. Now we can run the GMM based global refinement.
e2gmm_refine_iter.py r3d_00/threed_00.hdf --startres 3.9 --initpts threed_seg.pdb --sym c3
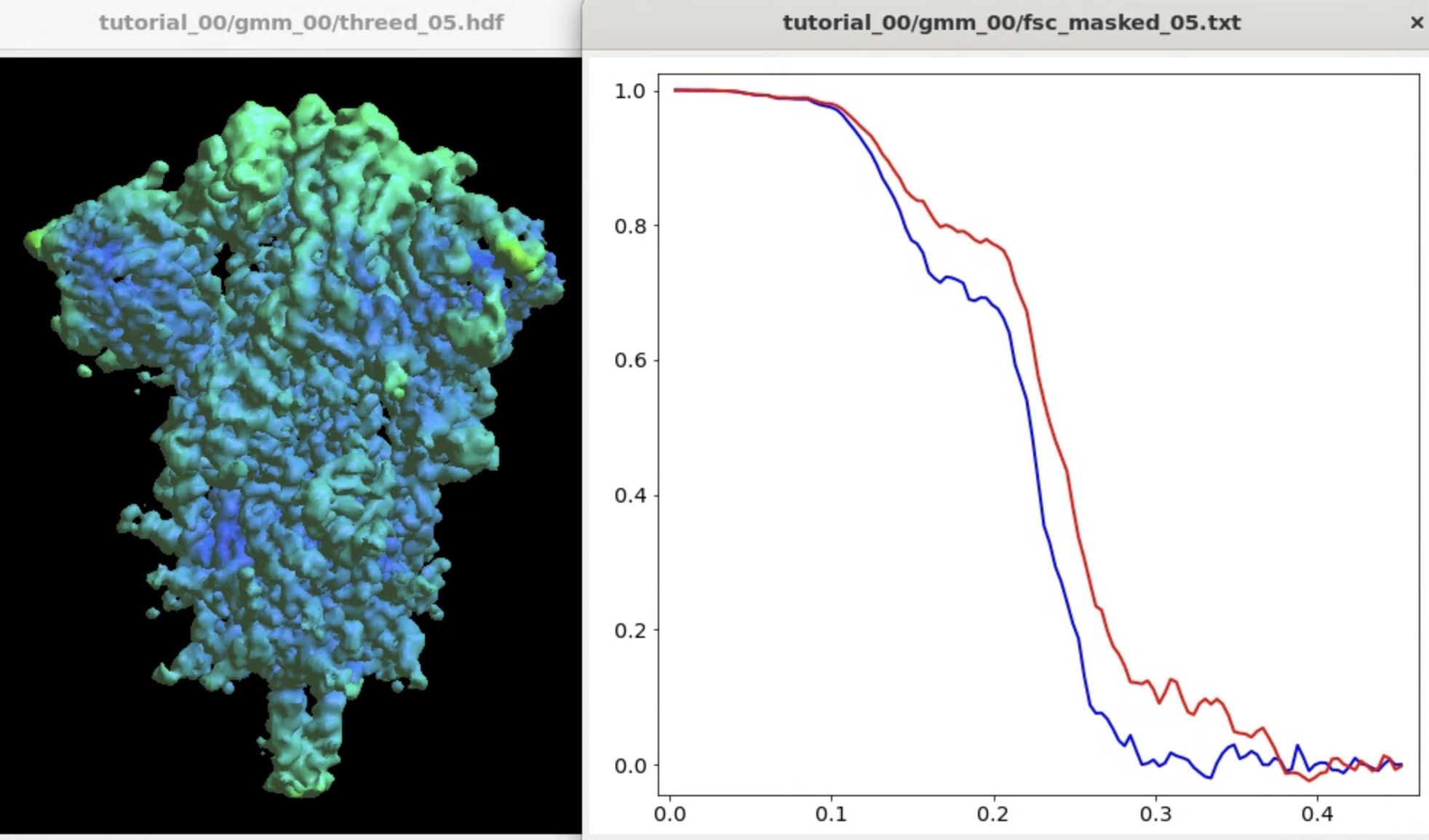
The program will start from the initial orientation assignment and run five iterations of refinement using GMMs as references. It should create a folder called gmm_00, and you can find all files related to the refinement inside. threed_xx.hdf are the reconstructed density maps, fsc_masked_xx.txt are the FSC curves, and model_xx_even/odd.txt are the GMM parameters after each iteration. After the refinement, the resolution should reach ~3.4Å.
Focused refinement
Here we target the RBD using focused refinement. First, we need to make a mask for the target region using Filtertool. In the e2display browser, select gmm_00/threed_05.hdf and click Filtertool to start the program. Hold Shift while clicking the button will enter a "safe mode" of Filtertool, which might be useful if the program crashes often. To craft a mask for the RBD, we use three processors:
mask.soft:dx=10.0:dy=15.0:dz=70.0:outer_radius=20.0:width=30.0 filter.lowpass.gauss:cutoff_abs=0.1 mask.auto3d.thresh:nshells=4:nshellsgauss=4:return_mask=True:threshold1=5.5:threshold2=3.0
mask.soft locates the rough location of one of the RBD, and filter.lowpass.gauss lowpass filters the density map. mask.auto3d.thresh creates the final mask based on the filtered density. Basically, it starts from a high threshold indicated by threshold1, at which only the density of the target domain is visible, and get down to a lower threshold2, where the density in the target domain is connected, but the density outside is not. The processor will then include all densities at threshold2 that are connected to the visible voxels at threshold1, pad a few layer and add a soft Gaussian falloff as indicated by nshells and nshellsgauss, then return the mask.
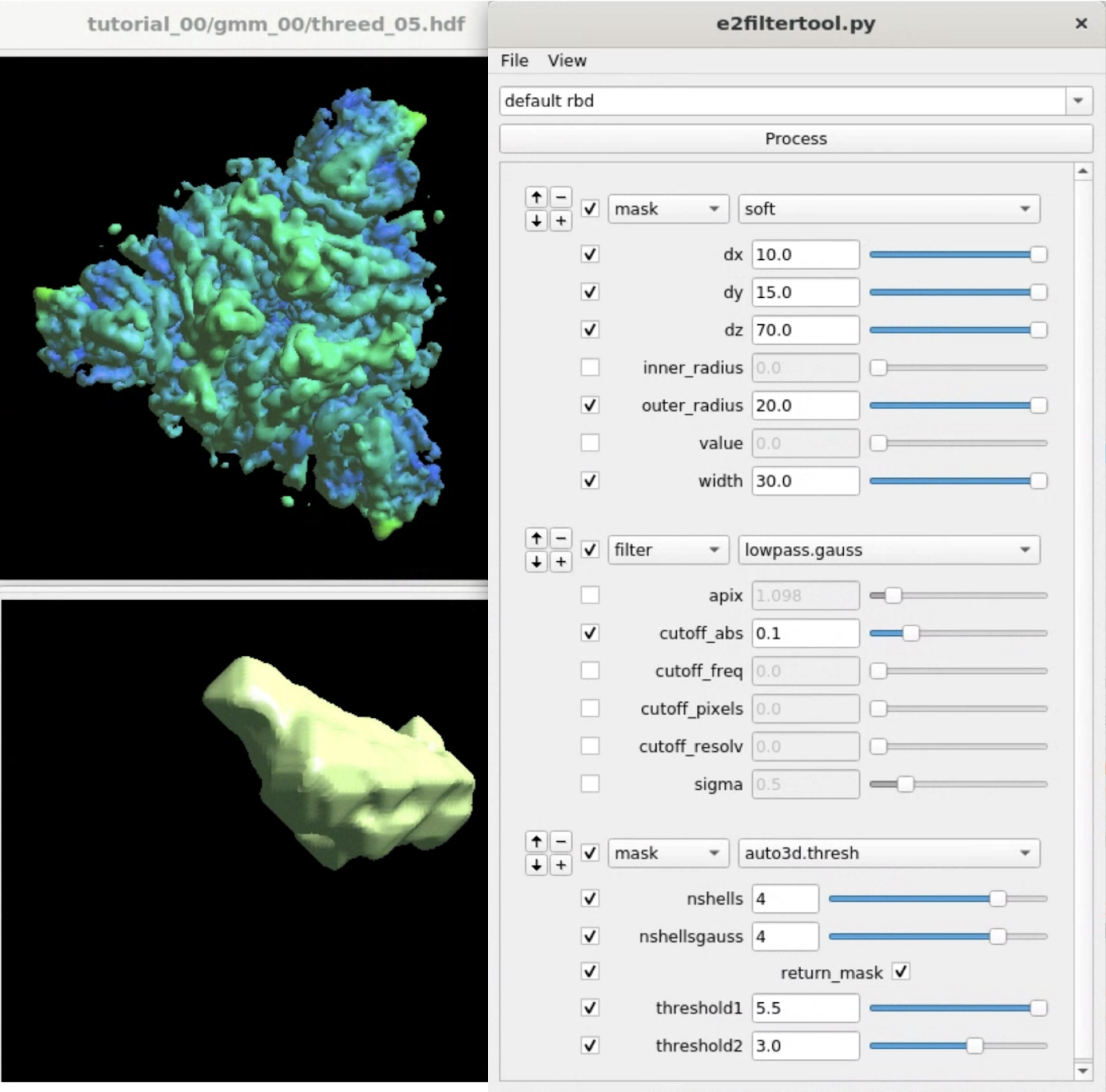
Clicking File -> Save will save the results to processed_map.hdf, and we rename it to mask_rbd.hdf for better bookkeeping.
Refine from a GMM heterogeneity analysis
e2gmm_heter_refine.py gmm_XX/threed_XX.hdf --maxres X --mask mask.hdf
Here we also start from the global refinement. --maxres defines the resolution for the heterogeneity analysis, and it is typically safer to use a lower resolution (7Å by default), since the flexible parts are often not well resolved in the first place. The target region is specified with mask.hdf.
Patch-by-patch refinement
Starting from a finished global refinement, run
e2gmm_refine_patch.py gmm_XX/threed_XX.hdf --startres X --npatch N
